
The air in the tube is pumped out to create a vacuum. The cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a hollow glass tube. These rays travel in straight lines and can be deflected by electric and magnetic field. What are cathode rays? Cathode rays are streams of electrons emitted from the cathode (the electrode connected to the negative terminal of a battery). His experimental results were further investigated by Rutherford and Bohr, which further provided important insights into the atomic world.īefore directly jumping Thomson's findings, let us understand some basic knowledge on cathode rays and the cathode-ray tube. However, Thomson's contributions remain more significant than the rest. Thomson was not the only one working on cathode rays, but several other players like Julius Plücker, Johann Wilhelm Hittorf, William Crookes, Philipp Lenard had contributed or were busy studying it.
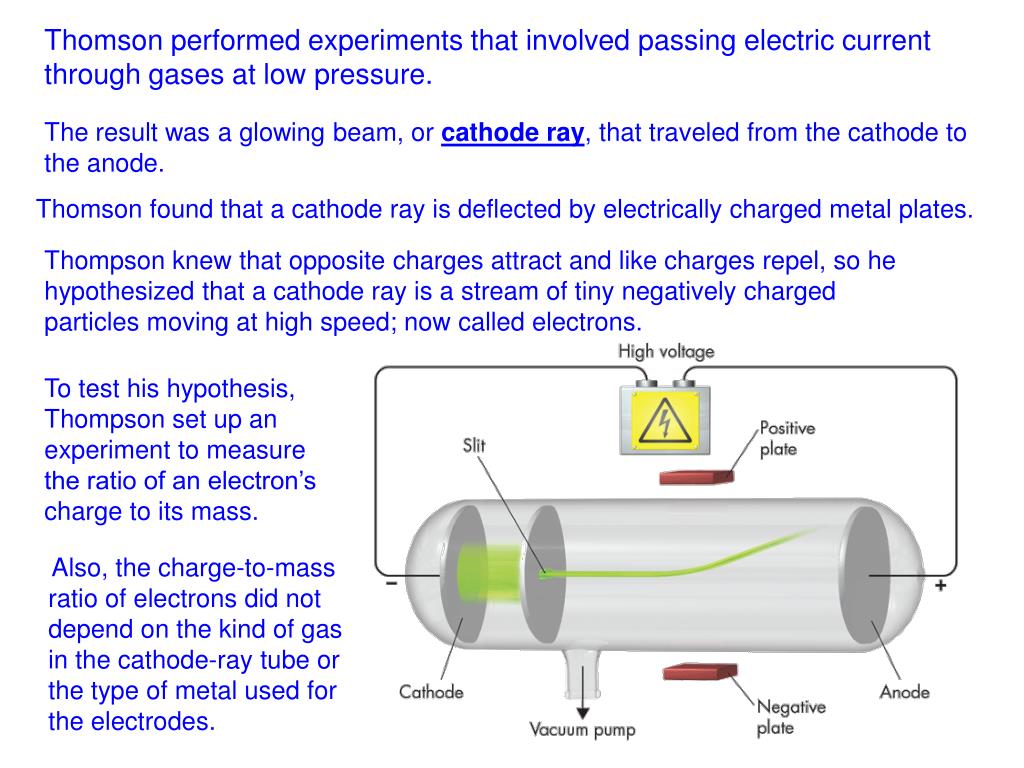
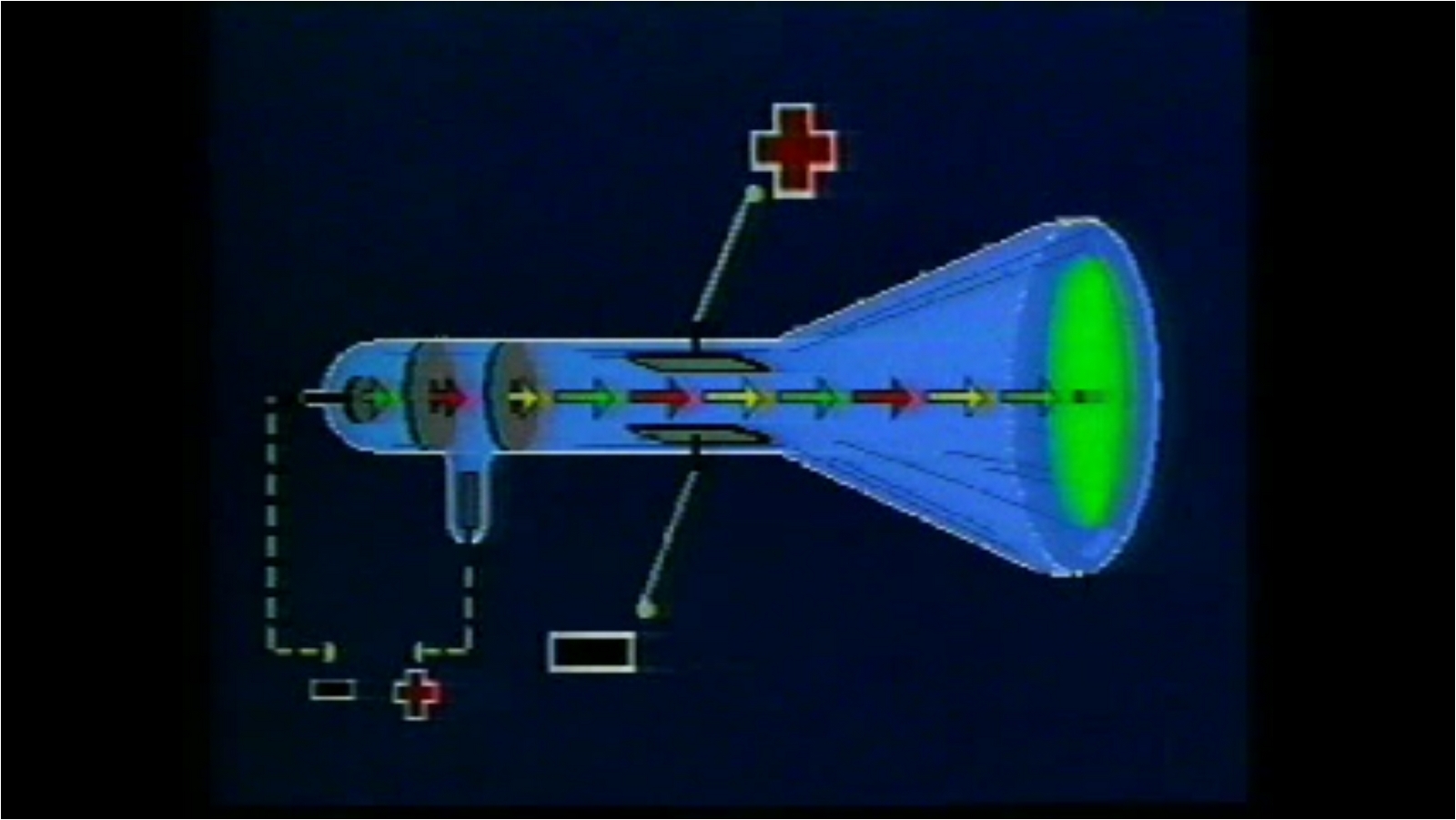
The apparatus of his experiment is called the cathode-ray tube (CRT).

These particles later were named electrons. In 1897, he showed that cathode rays were composed of very small negatively charged particles. He was well-known for the discovery of the electron. The image and video below show this experimental test.Sir Joseph John Thomson was a British physicist and Nobel Laureate. By applying a voltage between 500 and 800 V, a clear deflection of the beam may be obtained. This experimental test can also be easily carried out with our cathode tube, as it is provided with a pair of deflection plates positioned close to the beam. The force is proportional to the intensity of the electric field, and is directed in the opposite direction since the charge of the electron is negative, as shown in the picture below. The cathode ray beam is obviously sensitive to electric fields as well. The image and video below show this experimental test. This phenomena can be easily verified by using our cathode tube and a permanent neodymium magnet: by approaching the magnet to the tube, the beam is deflected low or upward depending on the polarity of the magnet. The picture below illustrates the effect of Lorentz interaction. Given the vector product between v and B, the force is perpendicular to both the direction of the magnetic field and the velocity direction. In our case, the electric field is null and the moving charged particles are electrons, so the formula becomes: Generally speaking, the force exerted on a charge q moving with speed v within a magnetic field B and electric field E, is calculated with the following formula : These are therefore negatively charged moving particles in a straight line, as such they are subject to the Lorentz force, which governs the motion of charged particles within magnetic fields. Magnetic DeflectionĪs we know, cathode rays are made up of electrons that are accelerated from the cathode to the anode.
#Thomson cathode ray experiment lorentz law generator
The high voltage generator is a compact module easily available online, however you can use any HV generator, such as the ones based on diodes and capacitors in Cockcroft-Walton voltage multiplier configuration. The high voltage between anode and cathode is obtained with a HV generator powered with a 12 V, it generates a voltage value of 10 KV. Two plates, used to demonstrate the influence of an electric field on the electron beam, complete the fixture.
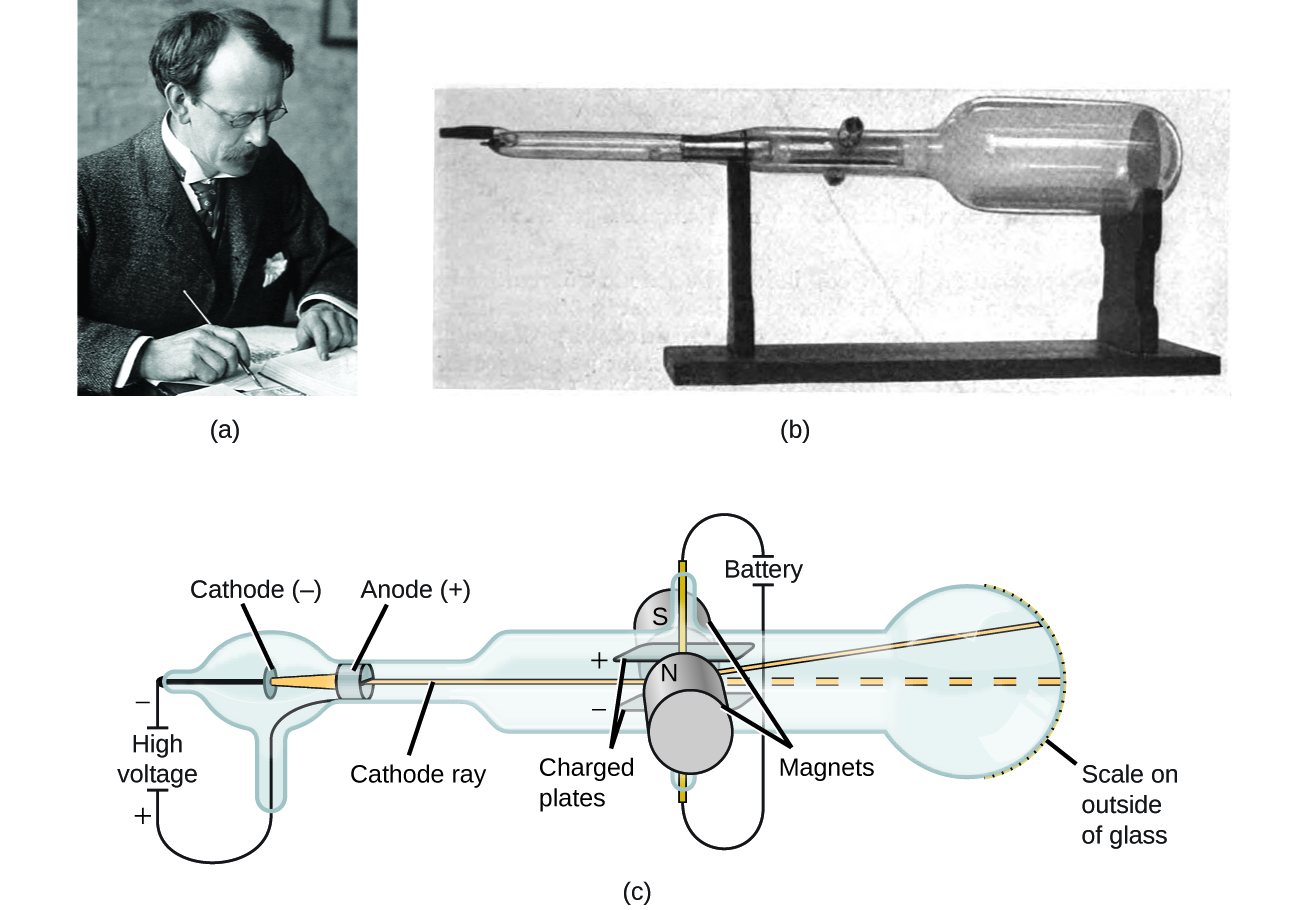
It is a tube equipped with cathode and anode, with a mask with a slit so as to produce a planar cathode ray beam, there is also a fluorescent screen so as to highlight in a visual manner the presence of the beam. The picture below illustrates the operation of a Crookes tube in a schematic way.įor experiments with cathode ray tube we used an educational model readily available on eBay. The term Crookes tube is also used for the first generation, cold cathode X-ray tubes, which evolved from the experimental Crookes tubes and were used until about 1920. Wilhelm Röntgen discovered X-rays using the Crookes tube in 1895. Crookes tubes are now used only for demonstrating cathode rays. Thomson’s 1897 identification of cathode rays as negatively charged particles, which were later named electrons. It was used by Crookes, Johann Hittorf, Julius Plücker, Eugen Goldstein, Heinrich Hertz, Philipp Lenard and others to discover the properties of cathode rays, culminating in J.J. When a high voltage is applied between the electrodes, cathode rays (electrons) are projected in straight lines from the cathode. A Crookes tube is an early experimental electrical discharge tube, with vacuum, invented by English physicist William Crookes and others around 1869-1875, in which cathode rays, streams of electrons, were discovered.ĭeveloped from the earlier Geissler tube, the Crookes tube consists of a partially evacuated glass bulb of various shapes, with two metal electrodes, the cathode and the anode, one at either end.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
